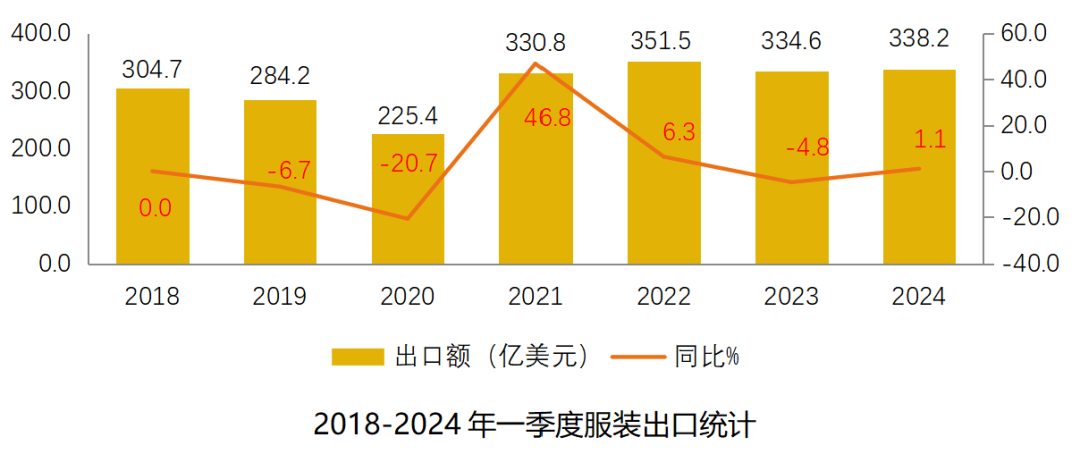
According to the latest data released by the China Textile Import and Export Association, China’s clothing exportsined a steady growth trend in the first quarter of 2024, with cumulative exports totalling $338,2 billion, up 1.1 percent, compared with the same year.
Specifically, although the export ratio in March decreased by 17.9%, mainly due to the high base effect caused by the centralized shipment of goods after the epidemic of the same period last year, compared with the same period of 2019 before the epidemic, the export scale in March this year still achieved a 25.1% growth, showing the long-term growth trend of Chinas clothing exports.
In terms of product segmentation, the performance of weaving clothing in the first quarter was bright, with exports reaching $150.6 billion, up 3.2% compared to the same year, and exports grew by 48.7 million units, up 11.9%, although export prices fell by 7.8% compared to the same year. Though weaving clothing exports dropped slightly, at $145.5 billion, down 0.6% compared to the same year, exports still achieved 13.7% growth and export prices dropped by 12.6%.
In terms of market distribution, China’s exports to the U.S. and the EU grew by 1.9% and 0.9% respectively, showing stable demand in both markets. Especially for the U.S. market, exports amounted to $68.2 billion, representing 20.2%, and a small growth of 0.2 percentage points. Compared to that, exports to Japan fell by 8.7%, showing challenges in some developed markets.
China’s exports to the Belt and Road Co-Building Countries haveined rapid growth, with exports to ASEAN growing by 6 percent and exports to the five Central Asian countries rising by 27 percent, showing the growth potential of emerging markets in China’s clothing exports.
In particular, underwear, such as weave T-shirts, shirts, underwear / sleeping shirts, breasts and other products, exports grew significantly in the first quarter, with weave T-shirts exports increased by 27.8%, shirt increased by 9.5%, underwear / sleeping shirts increased by 11.4%, and breasts increased by 9.8%. These data show that despite the slow recovery of global market demand, some clothing products in China are still able to find growth points in the highly competitive market.
In addition, the performance of some emerging markets and non-traditional markets is also worthy of attention. For example, exports to Vietnam grew by 11.5 percent, exports to Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan grew by 93.6 percent and Uzbekistan by 23 percent respectively. This trend indicates that Chinese clothing exports are diversifying their market layout and reducing dependence on the single market, which is important for resisting global economic volatility.
Overall, the external challenges facing Chinas garment industry remain severe, including uncertainty in international market demand, global economic friction and increased international competition, but by continuing to optimize product structure and market layout, Chinas garment industry is still expected to maintain steady export growth and maintain its competitiveness in the global market.


 Follow customer service WeChat
Follow customer service WeChat